Many people are still embarrassed or hesitant to talk about some illnesses.This is especially true for urogenital problems, which create discomfort and simultaneously also affect sexual activity.Over 70% of men do not seek medical attention in the early stages of the disease, while treatment is more effective if the disease is not too advanced.Identifying the symptoms of the disease early is important for prevention and early treatment.
What is prostatitis
The prostate or prostate gland is located in the center of the pelvis, connected to the bladder and the spermatic duct.The main function is the production of a substance responsible for the vitality and motility of spermatozoa.From a chemical point of view, this secretion is a basis of immunoglobulins with the addition of vitamins, zinc, iodine, the basis for the nutrition and activity of spermatozoa.The composition of the fluid is an important diagnostic parameter that helps to recognize symptoms at an early stage.
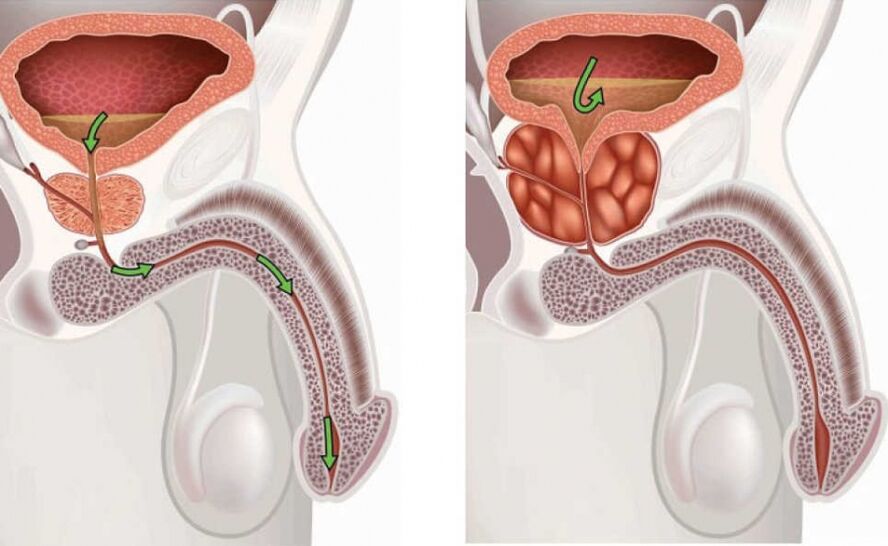
As you might guess from the name, the disease involves inflammatory processes in the prostate gland.This pathology is always associated with the presence of a bacterial infection, even if it does not necessarily present itself in a form recognizable to humans.The type of progression of the disease largely depends on age, predisposition, associated factors and characteristics of the body.
Normally the prostate gland does not make itself felt and does not attract attention.However, despite its rather deep location in the pelvic area, this organ is one of the most vulnerable in the male body.It is believed that only older people can experience the symptoms of prostatitis, but this is not true: the disease is typical for mature men between the ages of 20 and 60.
At an early stage, it is quite difficult to identify the disease.The signs may appear occasionally, then bother, then disappear without a trace.Doctors point out that the psychology of men, especially young men, also plays a role: not everyone is ready to go to the doctor and admit a "shameful" illness.
At the same time, the disease is characterized by dangerous complications, including:
- Infertility due to reduced sperm motility.Sometimes asymptomatic or mild chronic prostatitis becomes the only reason for the absence of a child in a couple.A woman can undergo tests as much as she wants, but this will not help until her husband decides to be tested himself for his ability to fertilize.
- Prostate adenoma is a benign tumor, which however can become very dangerous for men.This is due to the anatomical structure: the urinary system and vas deferens are positioned in such a way that if the prostate gland grows abnormally, it interferes with normal urination.There is a risk of a huge number of complications, including bladder rupture.
- Prostate cancer is, according to statistics, one of the most common diseases in men.Oncological diseases represent one of the ten main causes of death for people over 50;It is at this age that long-standing chronic prostatitis tends to degenerate into a life-threatening condition.
- Psychological problems associated with erectile dysfunction, infertility, problems with natural functions.This is a collateral symptom, but also significantly affects the patient's quality of life.
One in twenty men over thirty and more than half of those over fifty have experienced symptoms of prostatitis.This is one of the most common diseases.Prevention, early diagnosis and careful treatment can alleviate attacks and complications of the disease.
Acute (bacterial)
The disease can appear in men of any age.And if chronic forms of this disease are more typical for older people, then acute bacterial types of the disease can theoretically manifest themselves in anyone.The bacteria that cause signs of prostatitis can be pathogenic or opportunistic.
Here are some things to remember about this form:
- You can contract the infection at any age, even through unprotected sexual intercourse.
- Prostatitis is not the same as classic sexually transmitted diseases (STIs), such as gonorrhea, syphilis, chlamydia, but can occur as a secondary infection against the background of another disease.
- You can get the infection from your partner if she is sick with candidiasis, ovarian inflammation, vulvitis or vulvovaginitis, or you can pass the infection on to her.It happens that one of the spouses becomes a "carrier" of infection, and constant mutual reinfection is possible even within a constant couple.
- The main cause of acute bacterial prostatitis is unprotected sexual intercourse, followed by hypothermia and other situations that reduce local immunity.
Chronic bacterial
In the absence of adequate treatment and ignoring the symptoms in its acute form, as well as with regular reinfection, there is a high risk of developing a chronic pathological process.This is due to the fact that the prostate gland is a convenient place for the proliferation of pathogenic organisms: high temperature, humidity, nutrients.Chronic prostatitis is characterized by exposure to opportunistic strains that cause a slow but uncomfortable reaction that significantly worsens quality of life.
Characteristics:
- Paroxysmal course: the symptoms are almost no different from the acute form, but if it appears initially, the chronic form recurs regularly.Many people try to relieve the symptoms of prostatitis in men with pain relievers and other emergency methods.It works, but it doesn't solve the problem.
- After all, the symptoms often disappear on their own, without additional therapeutic methods, especially in young people: the body suppresses bacterial activity using the resources of its own immunity.As a rule, it is not possible to completely destroy the infection, so the relapses return again and again.Each one can become heavier than the previous one.
- Relapses are dangerous due to the appearance of purulent foci and damage to nearby organs: bladder, penis, testicles, kidneys.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis is the most common type of disease.Some men suffer from it for years, relieving attacks with painkillers, but without eliminating the underlying problem.Over time, the condition worsens.
Chronic non-bacterial
Treatment of prostatitis of this form will always be one of the most difficult.The disease is not associated with the activity of bacteria, which also makes diagnosis and identification of provoking factors difficult.Its causes are extremely varied: from an unhealthy lifestyle to working conditions associated with heavy lifting - for example, it is often found among loaders, builders and other people whose professional activities are related to such activities.
An attack of the disease can be triggered by neurological problems, stress, poisoning, injury to the prostate and pelvic muscles - this occurs in professional athletes.In many cases it is treatable.Often the etiology remains unclear.
Chronic asymptomatic
Another "insidious" type of prostatitis in men, as it develops without symptoms characteristic of the disease, as a result of which a person does not suspect that he has the disease.The reasons may be different, but most often they are associated simultaneously with the activity of bacteria and lifestyle features.
The biggest risk is that without symptoms it rarely occurs to a person to get tested.In this regard, doctors recommend that people over 40 years of age undergo preventive diagnosis: donate urine for the contents of leukocytes, as well as fluid secreted by the prostate.Asymptomatic prostatitis is becoming one of the most common causes of male infertility.
Causes of the disease
The most obvious cause of symptoms is bacteria entering the genitourinary tract.Systemic urogenital infections are extremely common, that is, a person simultaneously suffers from, for example, pyelonephritis.
Among the predisposing factors:
- unhealthy lifestyle - poor nutrition, alcohol abuse, excess weight is believed to also contribute to the development of the disease;
- hypothermia;
- irregular or promiscuous sexual life;
- unprotected sexual intercourse with people who may be carriers of the infection;
- physical inactivity, constant sitting position - prostatitis is typical for professional drivers;
- lesions in the pelvic area.
The main factor always remains age: if twenty-five year old men suffering from prostatitis are not so many, after fifty - more than half of all males.The quality of treatment for prostatitis depends on early diagnosis, so after forty years everyone should visit a doctor for examination.
Symptoms
The intensity of the symptoms depends on the form of the disease.We must not forget about the asymptomatic type, which does not manifest itself at all, but also has a destructive effect on health.You should consult a doctor for prostatitis medicines if the following symptoms appear:
- pain, burning during urination;
- painful sexual intercourse, deterioration of potency;
- pain during bowel movements;
- difficulty urinating - a dangerous symptom that causes stones;
- high temperature - in acute form;
- blood in urine, semen.

All signs vary in intensity.Treatment of prostatitis must begin with diagnosis;even just one of these manifestations is a reason for a medical examination.Painful sensations can change location, but are most often felt in the lower abdomen and rectum.In acute cases they are unbearable, increased pain is a bad sign, indicating a purulent form of the disease.
Diagnostics
To treat prostatitis, a correct diagnosis is necessary.The patient is sent for a general urine test to identify the leukocyte formula, which indicates the presence of inflammation.Be sure to check your blood and sperm - this helps determine sperm activity and often reveals infertility.Prostate secretions are taken for analysis and a smear to identify specific pathogens and prescribe antibiotics for prostatitis.
Treatment
Methods for treating prostatitis are complex and include physical therapy, medicinal techniques, correction of the patient's diet and lifestyle.Even advanced chronic forms can be treated without serious complications if recommendations and adequate therapy are followed.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is used for chronic forms and is prescribed only by the doctor, since in some cases it is contraindicated.
Among the methods, the most effective are the following:
- prostate massage: helps to get rid of congestion;
- heating in hot baths;
- ultrasound therapy;
- electropheresis;
- acupuncture.
The technique depends on the type of disease and the condition of the body.For example, heating to high temperatures and acute forms are contraindicated;it is necessary to first carry out therapy with drugs for prostatitis.
Drug
For pain in the perineum, prostatitis drugs with analgesic effect are prescribed.Bacterial forms require the use of antibiotics, and a specific drug is prescribed only after culture of BAC and identification of the sensitivity of microorganisms to a particular group.
Other drugs:
- Drotaverine - tablets for prostatitis to relieve spasms and pain;
- Tamsulosin is an alpha blocker, prostatitis tablets that improve smooth muscle contractions, improving urine flow;
Self-administration of antibiotics is contraindicated, but drugs from the cephalosporin group are often prescribed: they work well on almost all types of urogenital infections in men and women.
Candles
Rectal suppositories, also known as prostatitis suppositories, are excellent for relieving pain, inflammation and reducing all the discomforts associated with the disease.Most recommended by doctors:
- Prostate extract - suppositories for prostatitis with complex effect;
- Ketoprofen: relieves pain, swelling;
- Indomethacin.
Most medications are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.Taking it as a rectal suppository not only improves effectiveness but also helps minimize side effects.
Diet
Diet therapy also becomes part of the overall treatment strategy.Overweight people are advised to normalize their weight to eliminate congestion in the pelvic area.It is prescribed to exclude fatty foods, limit carbohydrates and avoid alcohol, which is often not compatible with antibiotics.Seafood, nuts, avocados and lean meat are healthy if there are no other contraindications.A correct diet also helps prevent prostatitis.
Forecast
With a timely diagnosis, a complete recovery is possible.The most important thing is not to allow the disease to become chronic, otherwise complications are inevitable: from prostate adenoma to cancer.In general, with adequate therapy and compliance with the treatment conditions by the patient, the prognosis is favorable.
Prevention
Prostatitis is a disease of "youth": recently it has also been diagnosed in adolescents, and men aged between thirty and thirty-five are increasingly faced with the problem.Therefore, prevention of prostatitis is important, which consists of:
- correct thermal regime: the pelvic organs must be neither overheated nor excessively cooled;
- avoid general hypothermia;
- sexual activity using personal protective equipment: condoms effectively block the path of bacteria;
- correct nutrition;
- Avoid both a sedentary lifestyle and irrational stress, especially those associated with lifting heavy objects.
All these methods will help prevent the development of an unpleasant disease.In older and older people, even in the absence of complaints, it is necessary to visit doctors from time to time: a urologist and an andrologist.